
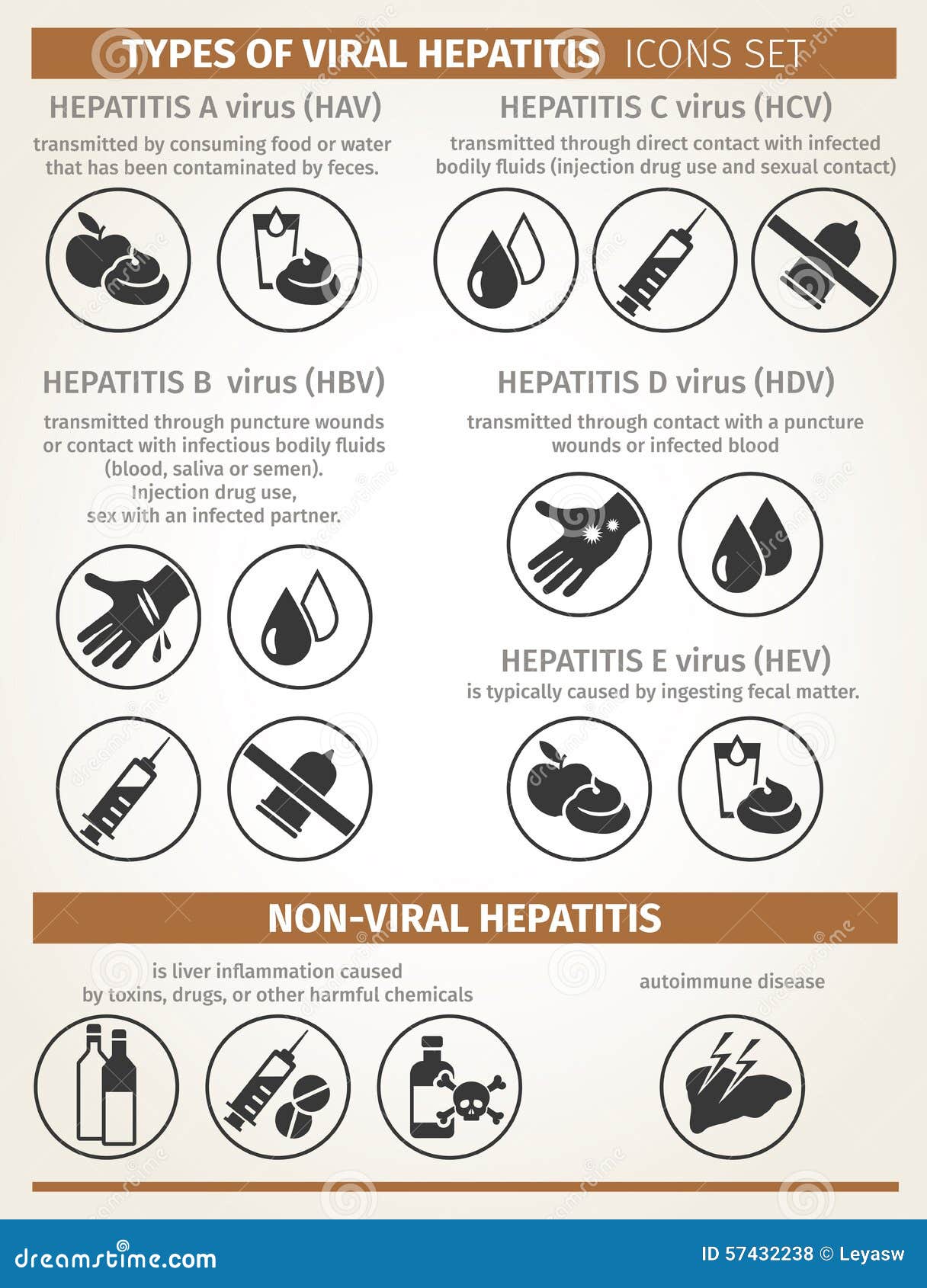
Overall, improvement of hygiene largely contributed to the decreasing trend in hepatitis A seroprevalence in the general population in Europe. Outbreaks that occur MSM may spread to the general population (« spillover ») through contacts with infected persons. Venues for casual sex, such as gay saunas and darkrooms have been implicated in large outbreaks. During sexual intercourses, contamination may occur during oral–anal, digito–anal and genito–oral sex with an infected partner. Hepatitis A is also commonly considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI) in men who have sex with men (MSM) with many reports since early 2000. In high income countries, hepatitis A is reported in travelers back from endemic areas, in foodborne outbreaks or in outbreaks that occur in closed settings (e.g school, crèches and minority ethnic groups). The period of infectivity usually starts 1 to 2 weeks before the onset of illness, while cases are still asymptomatic which is an aggravating factor for hepatitis A transmission and control. The reservoir of HAV is exclusively human and the transmission route is predominantly oro-fecal through the ingestion of contaminated water or food product and/or closed contact with an infected person. While often asymptomatic in children, jaundice may occur in up to 70% of adult cases and fulminant hepatitis in 1% of them. The mean incubation period is about 28 days but ranges between 15 and 50 days. Hepatitis A is an acute viral infection caused by the Hepatitis A Virus (HAV). The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. What's the difference: hepatitis B vs.Open AccessThis article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. Testing recommendations for hepatitis C virus infection.
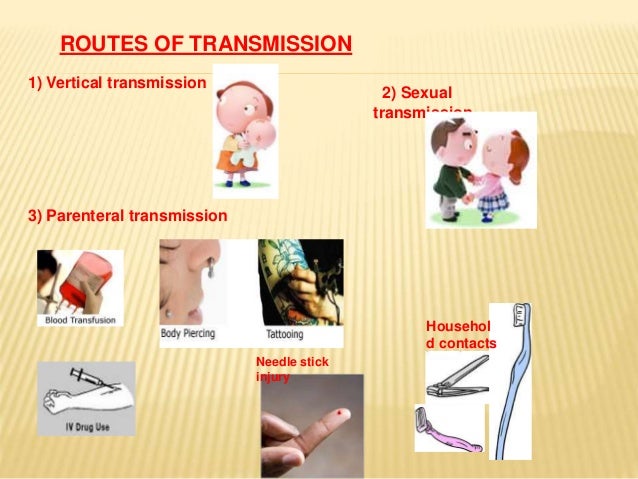
Blood safety basics.Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. doi:10.1002/rmv.1890Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention strategies for blood-borne viruses-in the era of vaccines, direct acting antivirals and antiretroviral therapy. Pfaender S, von Hahn T, Steinmann J, Ciesek S, Steinmann E. Understanding and addressing hepatitis C reinfection in the oral direct-acting antiviral era. 2014 4(1):38-39.įalade-Nwulia O, Sulkowski MS, Merkow A, Latkin C, Mehta SH. Sexual transmission of hepatitis C: a rare event among heterosexual couples. Hepatitis C questions and answers for the public.ĭodge JL, Terrault NA. Hepatitis C questions and answers for health professionals.Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexual transmission and viral hepatitis.Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. What is hepatitis C?Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis C prevalence estimates 2013-2016.Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Test for hepatitis C during every pregnancy.Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
